Trading View – TradingView is more than just a charting platform; it’s a vibrant ecosystem connecting traders worldwide. It offers powerful charting tools, a wealth of technical indicators, and a bustling community where ideas are shared and strategies are refined. This guide delves into TradingView’s core features, its social aspects, integration capabilities, pricing models, and potential limitations, providing a comprehensive overview for traders of all levels.
From creating and backtesting trading strategies to leveraging community insights and integrating with brokerage accounts, we’ll explore the many facets of this popular platform. We’ll also address common concerns and offer practical tips to maximize your TradingView experience. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting your trading journey, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to harness the full potential of TradingView.
TradingView Features and Functionality
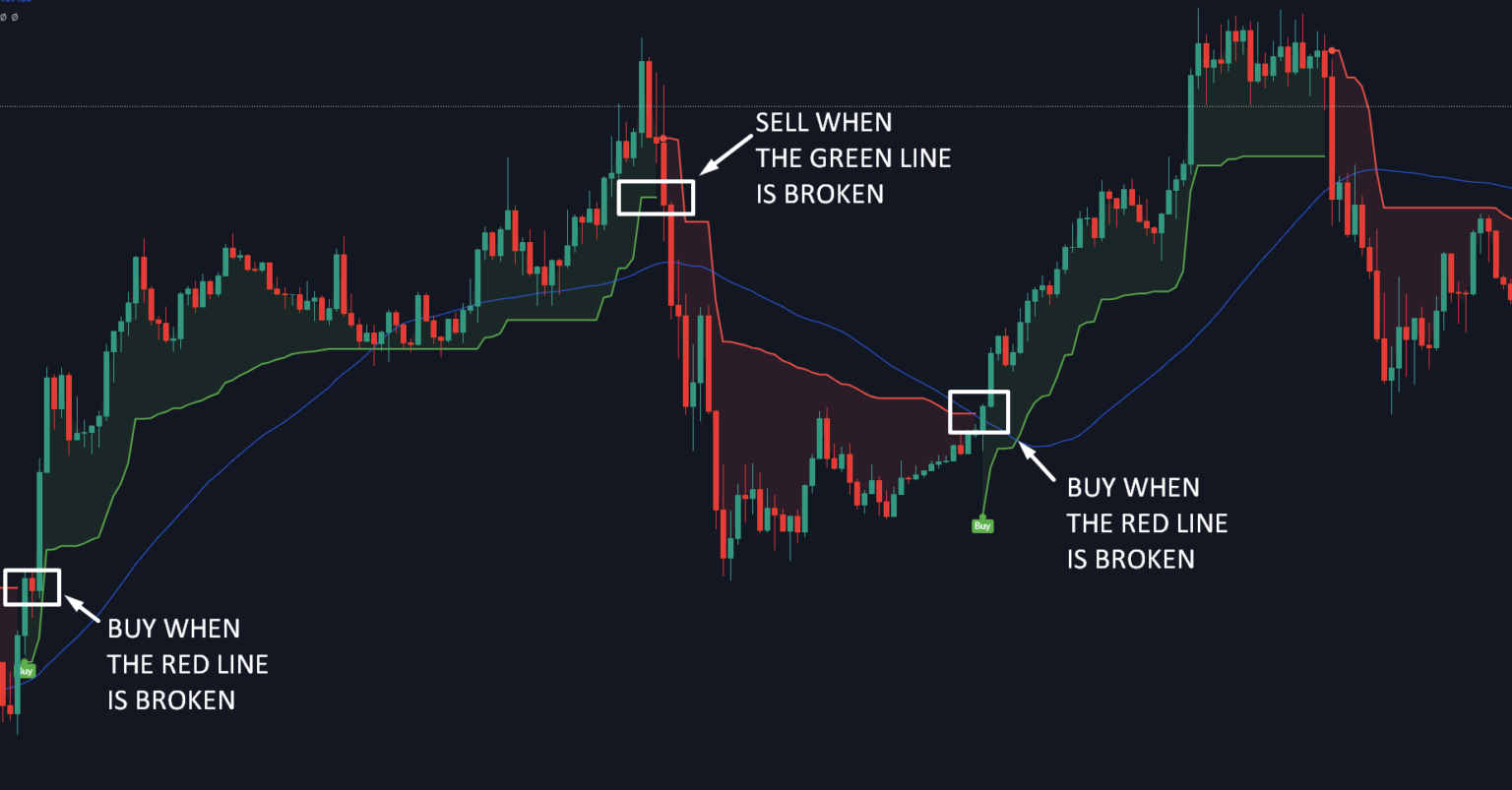
Source: easyforexpips.com
TradingView is a comprehensive platform for technical analysis and charting, offering a wide array of tools and features for traders of all levels. Its strength lies in its powerful charting capabilities, extensive indicator library, and surprisingly robust backtesting functionality, although with limitations. This section will delve into the specifics of these features and compare them to other popular trading platforms.
Charting Tools
TradingView’s charting capabilities are its core strength. Users can access a vast selection of chart types, including candlestick, bar, line, Heikin-Ashi, and Renko charts. Beyond basic chart types, powerful drawing tools allow for the creation of trend lines, Fibonacci retracements, support/resistance levels, and various geometric shapes to aid in pattern recognition. Interactive zooming and panning make navigating charts seamless, and customizable layouts allow traders to personalize their workspace.
Multiple timeframes can be displayed simultaneously, providing a holistic view of price action across different intervals. Importantly, TradingView offers a clean and responsive interface, even when dealing with complex charts and numerous indicators.
Technical Indicators, Trading View
TradingView boasts an extensive library of technical indicators, encompassing both classic and more advanced tools. Popular indicators like moving averages (SMA, EMA, WMA), RSI, MACD, Bollinger Bands, and Stochastic Oscillator are readily available. Beyond these staples, the platform provides access to hundreds of other indicators, many contributed by the active TradingView community. This vast selection caters to a broad range of trading styles and strategies.
Users can easily add, remove, and customize the parameters of these indicators to fine-tune their analysis. The ability to easily script custom indicators further enhances the platform’s flexibility.
Backtesting Capabilities
TradingView’s backtesting functionality allows users to test their strategies against historical data. While not as comprehensive as dedicated backtesting platforms like MultiCharts, it offers a valuable tool for initial strategy evaluation. Users can simulate trades based on their chosen indicators and parameters, observing the potential profitability and risk associated with their strategy. However, it’s crucial to understand the limitations.
TradingView’s backtesting primarily focuses on price action and doesn’t account for slippage, commissions, or other real-world trading costs. Therefore, results should be interpreted cautiously and viewed as an initial assessment rather than a definitive performance prediction. Furthermore, the available historical data might not always be completely accurate or comprehensive, influencing backtesting results.
Comparison with Other Platforms
Compared to platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 and NinjaTrader, TradingView’s strength lies in its user-friendly interface and vast community-contributed resources. MetaTrader excels in its automated trading capabilities and robust API, while NinjaTrader is known for its advanced order management and backtesting features. TradingView, however, offers a superior charting experience and a more accessible environment for learning and sharing trading ideas.
The choice of platform often depends on individual trading needs and priorities. For instance, a scalper might prefer MetaTrader for its speed and order execution, whereas a swing trader might find TradingView’s charting tools and community analysis more beneficial.
Hypothetical Trading Strategy
This strategy uses only TradingView’s built-in tools to identify potential long entries in a trending market.
| Step | Action | Indicator/Tool | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify an uptrend using a 20-period EMA | Exponential Moving Average (EMA) | Price consistently above the EMA suggests bullish momentum. |
| 2 | Confirm the uptrend with the RSI | Relative Strength Index (RSI) | RSI above 30 confirms the absence of oversold conditions. |
| 3 | Look for a pullback to the EMA | Price Action, EMA | A temporary price dip towards the EMA provides a potential entry point. |
| 4 | Place a long order at the EMA or slightly above | Order Placement | Capitalizing on the expected continuation of the uptrend. |
TradingView’s Community and Social Aspects: Trading View
Source: wallpaper.dog
TradingView’s strength lies not only in its powerful charting tools but also in its vibrant and active community. This network of traders, analysts, and investors contributes significantly to idea generation, sentiment analysis, and collaborative learning, shaping the overall platform experience. The social features facilitate the sharing of insights, strategies, and market perspectives, creating a dynamic ecosystem where users learn from each other and collectively interpret market movements.TradingView’s community plays a crucial role in shaping market sentiment and generating trading ideas.
The constant flow of information, ranging from technical analysis to fundamental insights, provides a collective perspective that can be both insightful and influential. This collective intelligence can help individual traders refine their strategies, identify potential opportunities, and mitigate risks. However, it’s vital to approach community-generated content with critical thinking, acknowledging the potential for bias and inaccuracies.
Community Collaboration and Idea Sharing
Users leverage TradingView’s social features in numerous ways to foster collaboration. They share their chart setups, publish detailed analyses, and engage in discussions within script comments, idea pages, and dedicated forums. This collaborative environment enables users to learn from each other’s experiences, refine their trading strategies, and gain exposure to diverse perspectives. For example, a trader might post a complex chart pattern they’ve identified, prompting a discussion amongst the community that leads to the discovery of additional confirming indicators or alternative interpretations.
This collective brainstorming can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of individual trading decisions.
Potential Biases and Inaccuracies in Community-Generated Content
While the TradingView community offers invaluable insights, it’s crucial to recognize the potential for biases and inaccuracies. Community-generated content is often influenced by individual biases, emotional responses to market movements, and the inherent limitations of subjective interpretation. Confirmation bias, for example, can lead users to selectively focus on information that supports their pre-existing beliefs, while neglecting contradictory evidence.
Furthermore, the lack of verification and fact-checking in many community posts means that inaccurate or misleading information can easily spread, potentially influencing the trading decisions of less experienced users. Therefore, critical evaluation and independent verification of information are crucial.
Hypothetical Case Study: Community Insights Influencing a Trading Decision
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where community insights significantly influence a trading decision.
- Scenario: A trader is analyzing the price action of a particular stock, noticing a potential bearish head and shoulders pattern forming.
- Community Input: The trader posts their chart on TradingView, seeking feedback from the community. Several experienced users confirm the pattern, highlighting additional bearish indicators such as declining volume and negative RSI divergence.
- Alternative Perspective: Another user points out a potential bullish breakout pattern from a longer-term perspective, suggesting the bearish head and shoulders might be a temporary correction within a larger uptrend.
- Decision: Based on the preponderance of evidence supporting the bearish interpretation, and considering the potential risks associated with the bullish counter-argument, the trader decides to take a short position, hedging against the possibility of the bullish breakout.
- Outcome: The bearish prediction is correct, resulting in a profitable trade for the trader. However, this success does not negate the importance of thorough due diligence and risk management.
Example of an Insightful TradingView Chart
Imagine a chart displaying the price action of a cryptocurrency, overlaid with several technical indicators. The chart shows a clear ascending triangle pattern, a bullish formation indicating a potential breakout. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is approaching oversold levels, suggesting potential buying pressure. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) shows a bullish crossover, confirming the upward momentum. Finally, the volume profile shows increasing volume during the upward price movements, indicating strong buying interest.
The combination of these indicators paints a strong bullish picture, suggesting a potential breakout above the triangle’s resistance level, which could trigger a significant price increase. The chart’s annotations clearly label each indicator and its implications, enhancing its clarity and usefulness for other traders. This would be an example of an insightful chart that leverages TradingView’s tools to provide a comprehensive and well-supported trading idea.
TradingView’s Integration with Brokerages and Other Services
TradingView’s strength lies not only in its charting capabilities and community features but also in its ability to seamlessly integrate with various brokerage platforms and other financial services. This integration allows traders to execute trades directly from the platform, streamlining their workflow and enhancing trading efficiency. The level of integration varies depending on the brokerage, but the overall goal is to provide a unified trading experience.TradingView offers direct trading capabilities through its partnership with a range of brokers.
This means you can place and manage trades without leaving the TradingView interface. This integration is achieved through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow TradingView to communicate with the brokerage’s trading systems. The availability of direct trading depends entirely on your chosen broker and their integration with TradingView.
Direct Trade Execution from TradingView
Direct trade execution from TradingView significantly simplifies the trading process. Instead of switching between different platforms, users can place orders directly from their charts, benefiting from the real-time data and analytical tools available within TradingView. The process usually involves linking your brokerage account to your TradingView account. Once linked, you can place orders using the built-in order ticket within the TradingView platform.
This ticket will typically allow you to specify order type (market, limit, stop), quantity, and other relevant parameters. The order is then transmitted to your brokerage for execution. Note that the specific steps may differ slightly depending on your broker and TradingView’s current interface.
Comparison of TradingView’s Integration with Other Financial Data Providers
TradingView’s integration capabilities are competitive with other major financial data providers. While platforms like Bloomberg Terminal offer extensive integration features often tailored to institutional investors, TradingView distinguishes itself by providing a user-friendly interface with robust charting tools and a strong community aspect, often at a significantly lower cost. Other providers might focus more on specific data types or analytical tools, while TradingView strives for a broader, more accessible platform.
The ease of use and the breadth of its brokerage integrations are key differentiators.
Step-by-Step Guide: Integrating TradingView with a Hypothetical Brokerage
The following steps illustrate the general process of integrating TradingView with a brokerage platform. Remember that the specific steps may vary depending on your chosen broker.
- Account Setup: Ensure you have active accounts with both TradingView and your chosen brokerage.
- Brokerage Connection: Navigate to the TradingView settings or account management section. Look for an option to connect or link a brokerage account. This usually involves selecting your broker from a list of supported providers.
- Login Credentials: You will be prompted to enter your brokerage account login credentials (username and password). TradingView will typically utilize secure methods to transmit this information.
- Account Verification: Your brokerage may require additional verification steps, such as a one-time password or email confirmation, to ensure account security.
- Connection Test: Once the credentials are entered, TradingView will usually perform a connection test to verify the integration. A successful test will confirm that TradingView can access your account information and trading capabilities.
- Place a Test Trade: Before placing any significant trades, it’s recommended to place a small test trade to ensure everything is working correctly.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using TradingView with Automated Trading Systems
Using TradingView with automated trading systems (ATS) offers several advantages, including streamlined data access and simplified order execution. However, challenges exist, particularly concerning the reliability and speed of the API connection. Benefits: Automated trading strategies can directly leverage TradingView’s real-time data and charting capabilities for signal generation and order execution. This integration can lead to improved efficiency and potentially better trade execution speeds.
Drawbacks: API limitations or unexpected outages could disrupt the automated trading process. The reliability of the API connection is crucial for the uninterrupted operation of any ATS. Furthermore, the specific functionalities available through the API might restrict the complexity of the trading strategies that can be implemented. Thorough testing and monitoring are essential to mitigate these risks.
TradingView’s Pricing and Value Proposition
TradingView offers a range of subscription tiers to cater to diverse trading needs and budgets. Understanding the features and pricing of each plan is crucial for selecting the best option based on your individual requirements and trading style. This section will break down the different plans, highlight key features, and assess TradingView’s competitive pricing within the broader market.
TradingView Subscription Tiers and Features
TradingView’s pricing structure is tiered, offering varying levels of access to its platform’s features. The core functionality is available on the free plan, but paid subscriptions unlock advanced tools and capabilities. The plans typically include Basic, Pro, Pro+, and Premium, although specific features and pricing can change over time. It is always best to check TradingView’s official website for the most up-to-date information.
Feature Comparison Across TradingView Plans
The following table summarizes the key features available in each TradingView plan. Remember that these features are subject to change, so always consult TradingView’s official website for the latest details.
| Feature | Basic | Pro | Pro+ | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Watchlists | Limited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Technical Indicators | Limited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Alerting Options | Limited | Advanced | Advanced | Advanced, including mobile push notifications |
| Chart Types | Limited | Many | Many | Many, with advanced drawing tools |
| Strategy Tester | No | Yes | Yes, with advanced features | Yes, with advanced features and backtesting capabilities |
| Pine Editor Access | Limited | Full Access | Full Access | Full Access |
| Price | Free | $14.95/month (or less with annual billing) | $29.95/month (or less with annual billing) | $59.95/month (or less with annual billing) |
Value Proposition for Different User Profiles
TradingView’s value proposition varies depending on the user’s experience level and trading goals.
Beginners: The free plan provides a solid foundation for learning technical analysis. The ability to access a wide array of charts and basic indicators is sufficient for beginners to familiarize themselves with the platform and develop their trading strategies. Upgrading to Pro might be considered once a more robust set of tools is required.
Advanced Traders: Advanced traders will likely find the Pro, Pro+, or Premium plans more valuable. These plans unlock advanced features like the strategy tester, which is crucial for backtesting trading strategies, and offer more sophisticated alerting options for timely trade execution. The ability to use the Pine Editor to create custom indicators and strategies is also a significant advantage for this group.
Institutions: While TradingView doesn’t explicitly target institutions with a dedicated plan, the Premium tier, coupled with potential API integrations, could provide the robust charting and analytical tools necessary for institutional-level analysis and trading. The scalability and data capabilities offered at the higher tiers could be beneficial for large-scale operations.
TradingView’s Pricing Competitiveness
TradingView’s pricing is generally considered competitive within the market for charting and technical analysis platforms. While other platforms offer similar features, TradingView’s comprehensive suite of tools, user-friendly interface, and active community often justify the cost, particularly for users who heavily rely on charting and technical analysis. However, direct comparisons with competitors require considering the specific features needed and the overall value proposition of each platform.
The free plan also provides a compelling entry point, allowing users to evaluate the platform before committing to a paid subscription.
Limitations and Potential Drawbacks of TradingView
TradingView, while a powerful and popular platform, is not without its limitations. Understanding these limitations is crucial for responsible and effective trading. Over-reliance on any single platform, including TradingView, can lead to flawed decision-making and potentially significant financial losses. This section will explore several key areas where caution and independent verification are essential.
Limitations of TradingView’s Charting and Analytical Tools
TradingView offers a wide array of charting tools and indicators, but their accuracy and effectiveness depend heavily on the quality of the underlying data and the user’s interpretation. While the platform provides a vast selection of indicators, not all are equally reliable or appropriate for every trading strategy. Some indicators might generate conflicting signals, and the sheer number of choices can be overwhelming for novice traders.
Furthermore, the platform’s customization options, while beneficial, can also lead to the creation of overly complex and potentially misleading charts if not used judiciously. For example, a trader might over-optimize indicators to fit past price action, leading to poor predictive capabilities for future price movements.
Risks of Sole Reliance on TradingView for Trading Decisions
Relying solely on TradingView for trading decisions is inherently risky. The platform’s data, while generally reliable, is not infallible. Delays in data feeds, inaccuracies in data points, or even temporary outages can significantly impact trading decisions. Moreover, TradingView’s analysis tools are ultimately just tools; they do not guarantee profitable trades. Successful trading requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates fundamental analysis, risk management, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics, which go beyond the capabilities of any single platform.
For example, a trader might rely solely on a technical indicator suggesting a buy signal, neglecting fundamental news that indicates a negative outlook for the asset.
Examples of Inaccurate or Misleading Information on TradingView
While TradingView strives for accuracy, situations can arise where the information presented is inaccurate or misleading. This can stem from errors in data feeds, programming glitches in indicators, or even intentional manipulation by users sharing inaccurate or biased analyses on the platform’s social features. For instance, a wrongly configured indicator might generate false buy or sell signals, leading to losses.
Similarly, a user-created script with flaws could provide inaccurate backtesting results, leading to an overestimation of a strategy’s potential profitability. Another example could be a delay in receiving real-time market data, causing a trader to miss a crucial opportunity or enter a trade at an unfavorable price.
Importance of Independent Verification of TradingView Data and Insights
Independent verification of data and insights from TradingView is paramount. Never make trading decisions based solely on information from a single source. Always cross-reference data with information from multiple reliable sources, such as financial news websites, brokerage platforms, and official company announcements. Compare different indicators and analytical tools to get a more holistic view of the market.
This multi-faceted approach helps identify potential biases or errors in TradingView’s data and ensures a more informed and less risky trading strategy. For example, before acting on a buy signal generated by TradingView, compare the signal with the asset’s fundamental performance and check news sources for any relevant information that could impact the asset’s price.
Potential Risks and Mitigating Strategies When Using TradingView for Trading
It is crucial to understand the potential risks involved when using TradingView for trading and implement appropriate mitigating strategies.
- Risk: Inaccurate or delayed data leading to poor trading decisions. Mitigation: Cross-reference data with multiple reliable sources and use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis.
- Risk: Over-reliance on technical indicators without considering fundamental factors. Mitigation: Incorporate fundamental analysis into your trading strategy and avoid solely relying on technical signals.
- Risk: Misinterpretation of charting tools and indicators. Mitigation: Thoroughly understand the principles behind each indicator before using it and seek training if necessary.
- Risk: Influence by biased or inaccurate community opinions on the platform. Mitigation: Critically evaluate information shared by other users and verify it with independent sources.
- Risk: Over-optimization of trading strategies based on past performance. Mitigation: Employ robust out-of-sample testing and avoid overfitting your strategies to historical data.
Wrap-Up
TradingView stands as a powerful tool for both novice and expert traders, offering a rich set of features and a dynamic community. While it presents some limitations and requires critical evaluation of community-generated data, its charting capabilities, indicator library, and brokerage integrations make it a valuable asset in any trader’s arsenal. By understanding its strengths and weaknesses, and by employing sound risk management practices, you can effectively leverage TradingView to enhance your trading strategies and decision-making process.
